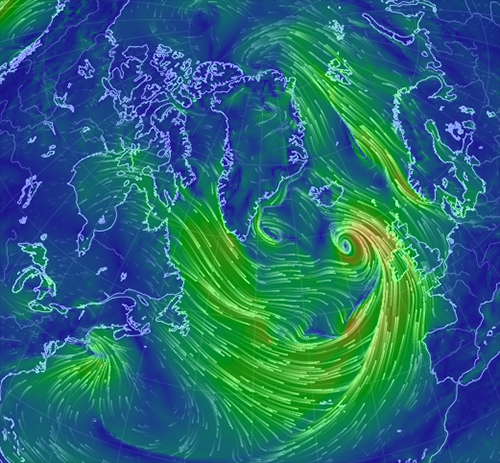
The storm that rampaged thru Texas and wreaked havoc across the south and midwest is winding up to deliver a hot blow to a suddenly vulnerable-even-in-December Arctic.
As it departs North America this week, the storm will rapidly intensify over the northern reaches of the Gulf Stream and draw tremendous amounts of warm air northward from Spain and the Mediterranean Sea toward the Arctic. As the storm approaches Iceland, it will have strengthened to the equivalent of some of the strongest hurricanes ever recorded in terms of atmospheric pressure. Intensely high pressure over western Russia, perhaps boosted by melting sea ice, will aid in setting up the tropics-to-pole atmospheric superhighway.
Unlike other recent episodes of extreme weather around the planet, this storm is probably not related to El Niño, which has limited influence in Europe. The storm will be strengthening over the exact spot that North Atlantic temperatures have been cooling over recent years, an effect that scientists have linked to a slowdown of the basin’s circulation triggered in part by melting sea ice—the same scenario that was highly dramatized in the movie The Day After Tomorrow. This year, there’s been a notable increase in the sharp contrast between this cold patch and record warm ocean temperatures in the tropical Atlantic, an effect that leads to stronger ocean storms—like this one.
The remarkable storm will briefly boost temperatures in the Arctic basin to nearly 10 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than normal—and the North Pole itself will be pushed above the freezing point, with temperatures perhaps as warm as 40 degrees. That’s absolutely terrifying and incredibly rare. Keep in mind: It’s late December and dark 24 hours a day at the North Pole right now. The typical average high temperature this time of year at the North Pole is about minus 15 to minus 20 degrees. To create temperatures warm enough to melt ice to exist in the dead of winter—some 50 or 60 degrees warmer than normal—is unthinkable.
For some perspective, I contacted a team of climate scientists at the University of Washington who maintain a fleet of weather monitoring equipment near the North Pole. James Morison, the principal investigator of the North Pole Environmental Observatory, said he’s “never heard of” temperatures above freezing in the wintertime there. Looking closer at the weather data, it appears this event is in fact unprecedented during the time period from late December through late April.
http://climatecrocks.com/2015/12/29/most-terrifying-weather-ends-a-hot-2015/On Wednesday, the North Pole will be warmer than Western Texas, Southern California, and parts of the Sahara.